How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Transform Your Garden with Expert Tips – Roses, with their captivating beauty and intoxicating fragrance, have long been cherished for their ability to adorn gardens with vibrant color and timeless elegance. But acquiring these prized blooms can sometimes be a costly endeavor.
Fortunately, the art of rose propagation offers a rewarding and economical alternative, allowing you to expand your rose collection with ease and precision. This comprehensive guide will empower you to transform your garden into a fragrant paradise, brimming with the exquisite blooms of your own creation.
From selecting the perfect cuttings to nurturing their growth, we’ll explore the essential steps involved in successfully propagating roses. Discover the secrets to identifying healthy cuttings, the ideal time for taking them, and the proper techniques for preparing them for rooting.
We’ll delve into the various rooting methods, including both water and soil propagation, and provide expert guidance on creating the optimal environment for successful root development. Through meticulous care and attention, you’ll witness the transformative journey of your cuttings as they develop into thriving rose plants, ready to grace your garden with their captivating beauty.
Introduction to Rose Propagation: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Transform Your Garden With Expert Tips
Rose propagation from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden or share your favorite varieties with friends. This method allows you to create new rose bushes from existing plants, preserving their unique characteristics and ensuring genetic continuity.
Benefits of Propagating Roses from Cuttings
Propagating roses from cuttings offers several advantages over purchasing new plants:
- Cost-effectiveness:Creating new rose bushes from cuttings is significantly cheaper than purchasing them from nurseries or garden centers.
- Genetic preservation:Cuttings produce exact replicas of the parent plant, ensuring you maintain the desired characteristics of your favorite rose variety.
- Increased availability:Propagating roses from cuttings allows you to multiply your collection quickly and efficiently, increasing the number of rose bushes in your garden.
- Personal satisfaction:There is a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction in successfully propagating roses from cuttings, knowing you created new life from existing plants.
Types of Rose Cuttings
The success rate of rose propagation depends largely on the type of cutting used. Different types of cuttings are best suited for specific times of the year and offer varying degrees of success:
- Softwood cuttings:Taken from new growth in spring or early summer, these cuttings are flexible and have not yet hardened. They are typically easier to root but require more care and protection.
- Hardwood cuttings:Taken from mature, dormant wood in late autumn or winter, these cuttings are more difficult to root but are more resilient and can be stored for longer periods. They are best suited for propagation of shrub roses and other hardy varieties.
- Semi-hardwood cuttings:Taken in late summer or early autumn, these cuttings are a compromise between softwood and hardwood cuttings. They offer a balance of ease of rooting and resilience, making them suitable for a wide range of rose varieties.
Essential Tools and Materials
To successfully propagate roses from cuttings, you will need a few essential tools and materials:
- Sharp knife or pruning shears:For clean and precise cuts to minimize damage to the cuttings.
- Rooting hormone:Helps stimulate root growth and increases the chances of successful rooting.
- Rooting medium:A well-draining mixture, such as a combination of perlite and vermiculite, provides the ideal environment for root development.
- Clear plastic bags or humidity domes:Create a humid environment to promote root growth and prevent dehydration.
- Containers:Small pots or trays are suitable for rooting cuttings.
- Labels:To keep track of the different rose varieties you are propagating.
Choosing the Right Cuttings
Selecting the right rose cuttings is crucial for successful propagation. By understanding the characteristics of healthy cuttings and choosing the appropriate time of year, you can significantly increase your chances of growing new rose plants.
Transforming your garden with the vibrant blooms of roses is easier than you might think. Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your collection. For detailed insights on the process, check out this comprehensive guide: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Expert Insights for Beautiful Blooming.
With the right techniques and a bit of patience, you can enjoy a garden overflowing with beautiful, fragrant roses.
Identifying Healthy Rose Cuttings
Healthy rose cuttings are essential for successful propagation. To identify healthy cuttings, look for the following characteristics:
- Vigorous Growth:Select cuttings from strong, healthy rose bushes that exhibit vigorous growth. Avoid cuttings from weak or diseased plants.
- Mature Wood:Choose cuttings from stems that have matured and hardened. These stems are typically brown or reddish-brown in color. Avoid using green, immature stems.
- Absence of Disease:Ensure the cuttings are free from any signs of disease, such as spots, discoloration, or pests.
Selecting the Best Time of Year for Taking Cuttings
The best time to take rose cuttings depends on your location and climate. Generally, the ideal time is during the dormant season, when the plant is not actively growing.
- Spring:In regions with mild winters, spring is an excellent time to take cuttings, as the plant is starting to awaken from dormancy.
- Late Summer/Early Fall:In areas with colder climates, taking cuttings in late summer or early fall, after the plant has finished flowering, can be successful.
- Avoid Hot, Humid Weather:Avoid taking cuttings during hot, humid weather, as this can increase the risk of disease and rotting.
Ideal Characteristics of a Good Rose Cutting
A good rose cutting should possess the following characteristics:
- Length:Cuttings should be 6-8 inches long.
- Nodes:Cuttings should have at least three nodes (the points where leaves or buds grow).
- Angle:Cuttings should be taken at a 45-degree angle just below a node.
- Leaves:Remove the leaves from the bottom two nodes to prevent rotting.
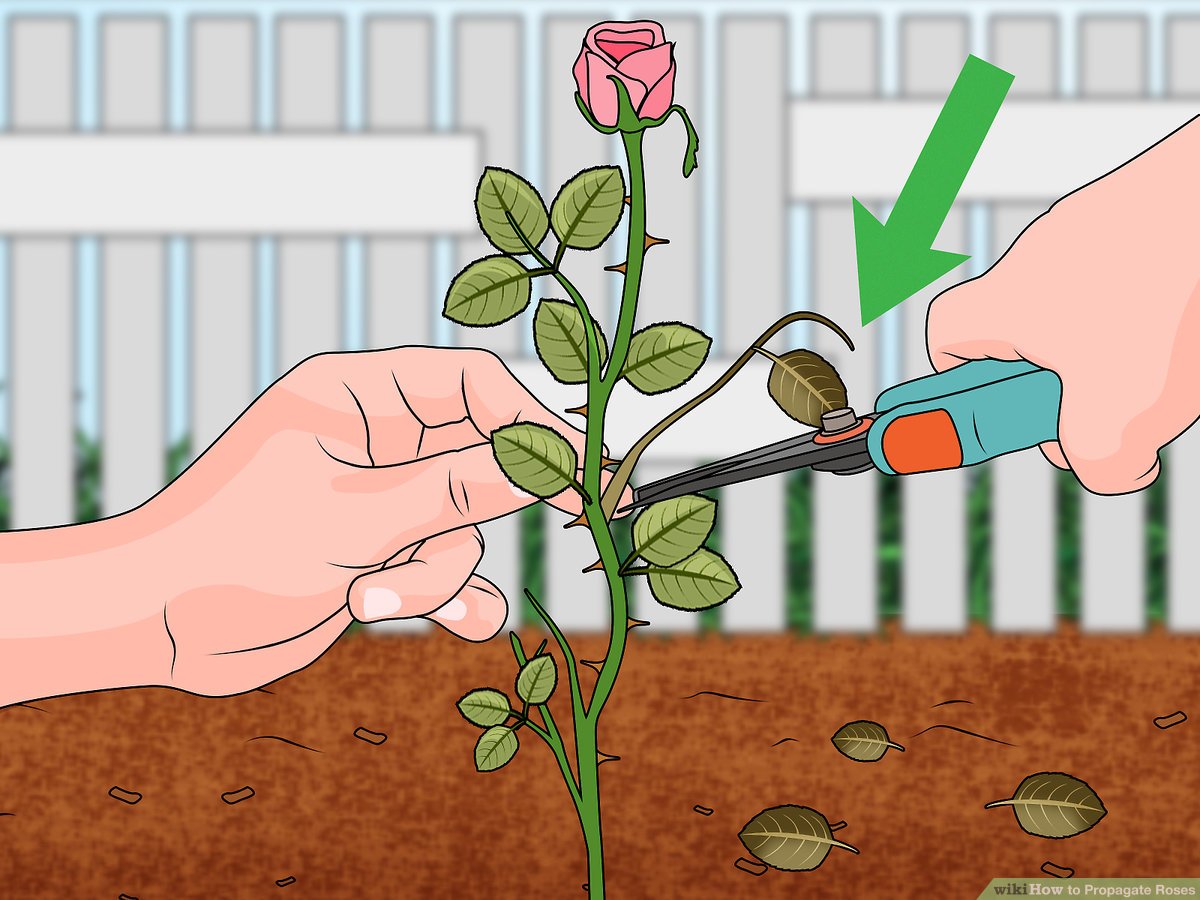
Preparing the Cuttings
After selecting the ideal rose cuttings, the next crucial step is preparing them for propagation. This involves making precise cuts, removing unnecessary parts, and treating the cuttings with rooting hormone to stimulate root growth.
Making Clean Cuts
Sharp, clean cuts are essential for successful rose propagation. Using a sharp, sterilized knife or pruning shears, make a clean, angled cut just below a node. A node is a point on the stem where leaves or buds grow.
The angled cut helps to increase the surface area for root development.
Make the cut at a 45-degree angle to maximize the surface area for root development.
Removing Leaves and Thorns
To prevent energy loss and potential disease, remove the leaves and thorns from the lower portion of the cutting. This is important because the leaves and thorns will draw energy from the cutting, hindering root development. Leave the top leaves intact as they are essential for photosynthesis and energy production.
- Remove all leaves below the first node.
- Trim any thorns present on the cutting to avoid injury and potential disease.
Treating with Rooting Hormone
Rooting hormone is a powder or liquid that contains plant hormones that stimulate root growth. Applying rooting hormone to the cut end of the rose cutting can significantly increase the chances of successful propagation. The hormone helps to promote cell division and root development.
- Dip the cut end of the cutting into the rooting hormone powder or liquid.
- Ensure that the hormone is evenly distributed across the cut surface.
- Avoid excessive use of rooting hormone as it can inhibit root growth.
Rooting Methods
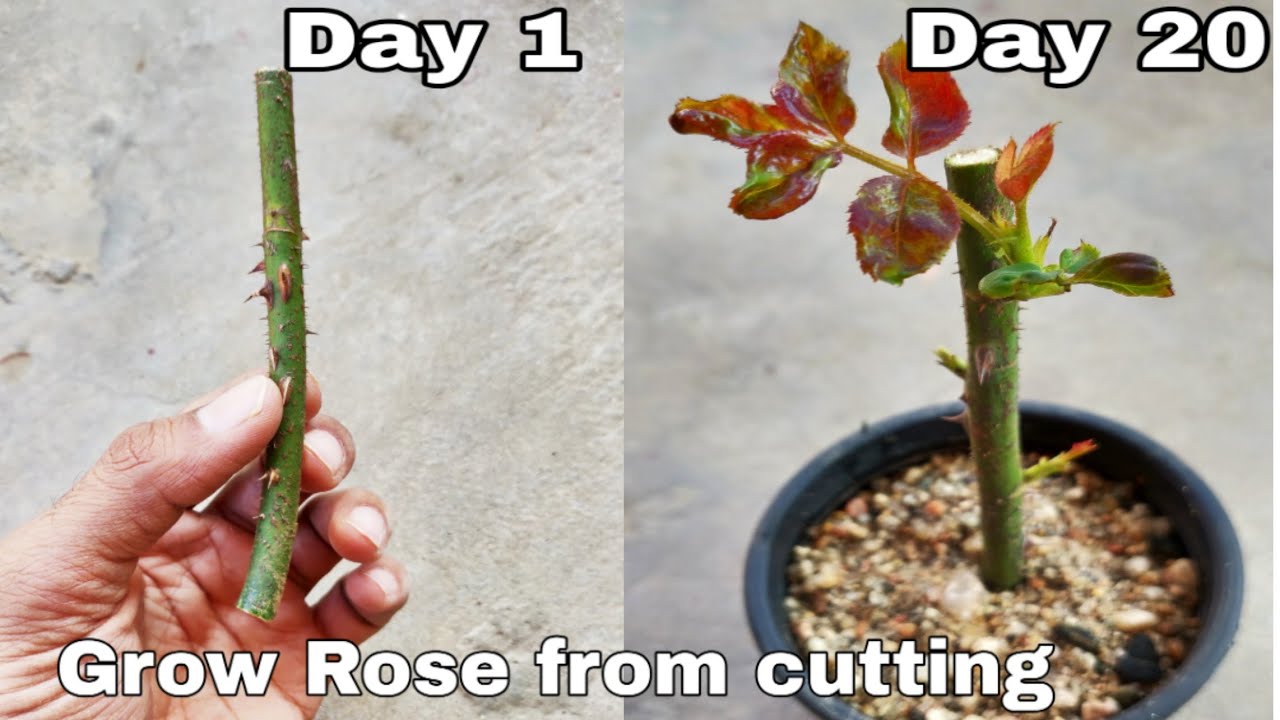

Rose cuttings can be rooted using various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The two most common methods are water propagation and soil propagation.
Water Propagation
Water propagation is a simple and straightforward method that allows you to observe root development. This method involves placing the rose cuttings in a container filled with water.
- Advantages: Water propagation is an easy and accessible method for beginners, as it requires minimal equipment and allows for easy observation of root development. This method is also less prone to fungal diseases, which can be a problem with soil propagation.
- Disadvantages: Water propagation can lead to weak roots, as the cuttings do not have to develop strong root systems to absorb water. This can make the cuttings more susceptible to stress when transplanted into soil. Additionally, the roots may become brittle and prone to breakage when removed from the water.
Soil Propagation
Soil propagation is a more traditional method that encourages the development of strong and healthy root systems. This method involves planting the cuttings in a well-prepared rooting medium.
- Advantages: Soil propagation promotes the development of robust root systems, making the cuttings more resilient and adaptable to different environments. It also allows the cuttings to establish themselves in a more natural setting, reducing the risk of shock during transplantation.
- Disadvantages: Soil propagation can be more challenging than water propagation, as it requires careful preparation of the rooting medium and monitoring of moisture levels. It also increases the risk of fungal diseases, especially if the soil is not properly sterilized or if the cuttings are overwatered.
Preparing a Rooting Medium
The choice of rooting medium is crucial for successful rose propagation. Both soil and water can be used as rooting mediums, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Soil
Soil is the most common rooting medium for roses. It provides a stable environment for the cuttings to develop their roots.
- Preparing the Soil: A well-draining soil mix is ideal for rooting rose cuttings. A mixture of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite is commonly used. The soil should be moistened before planting the cuttings.
Water
Water is a simple and readily available rooting medium. It allows for easy observation of root development.
Transforming your garden with the vibrant beauty of roses is easier than you think, thanks to the magic of propagation. Learn the secrets to successfully multiplying your rose collection by taking cuttings, a technique that allows you to create new plants from existing ones.
For a deep dive into the most effective methods, check out The Best Techniques for Propagating Roses From Cuttings: A Comprehensive Guide , which covers everything from choosing the right cuttings to ensuring successful rooting. With a little patience and these expert tips, you can easily propagate your own rose bushes and enjoy a garden bursting with fragrant blooms.
- Preparing the Water: Use clean, filtered water to prevent contamination and algae growth. Change the water every few days to maintain its freshness.
Planting the Cuttings
Once the rooting medium is prepared, the cuttings can be planted.
Soil Propagation
- Planting Depth: Plant the cuttings in the prepared soil mix, ensuring that at least two nodes are buried. The nodes are the points on the stem where leaves grow.
- Watering: After planting, water the cuttings thoroughly. Ensure the soil remains moist but not waterlogged.
- Humidity: Maintain a high level of humidity around the cuttings to promote root development. This can be achieved by covering the pot with a plastic bag or dome.
Water Propagation
- Container Choice: Use a clean glass or plastic container that is tall enough to hold the cuttings.
- Water Level: Fill the container with water, ensuring that the base of the cuttings is submerged.
- Light: Place the container in a bright location, but avoid direct sunlight, which can overheat the water.
Caring for the Cuttings
After you’ve successfully prepared your rose cuttings and started the rooting process, it’s crucial to provide the right care to encourage root development and ensure their survival. This involves maintaining proper moisture levels in the rooting medium, providing adequate light and warmth, and recognizing the signs of successful rooting.
Maintaining Moisture Levels
The rooting medium should be kept consistently moist, but not soggy. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while under-watering can cause the cuttings to dry out.
- Regularly check the moisture levels:Use your finger to check the moisture of the rooting medium. If it feels dry to the touch, it’s time to water.
- Water thoroughly:When watering, ensure the entire rooting medium is moistened. However, avoid over-watering, as this can suffocate the roots.
- Use a well-draining medium:A well-draining medium like a mixture of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite will help prevent waterlogging.
- Avoid watering from above:This can cause the leaves to become wet and susceptible to fungal diseases. Water the base of the cuttings instead.
Providing Light and Warmth
Rose cuttings need adequate light and warmth to thrive.
- Bright, indirect light:Rose cuttings should be placed in a location that receives bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can scorch the leaves.
- Warm temperatures:Rose cuttings root best in warm temperatures between 70-75 degrees Fahrenheit (21-24 degrees Celsius).
- Consider a heat mat:Using a heat mat can help maintain a consistent temperature and promote root growth.
Recognizing Signs of Successful Rooting
After several weeks, you should start to see signs of successful rooting.
- New growth:The emergence of new growth at the top of the cutting is a strong indicator of root development.
- Firmness:The cutting should feel firm and stable when gently tugged. This suggests the roots are anchoring the cutting in the rooting medium.
- Root development:If you carefully remove the cutting from the rooting medium, you may be able to see small, white roots emerging from the base.
Transplanting the Rooted Cuttings
Once your rose cuttings have developed a robust root system, it’s time to move them to their permanent location in your garden. This is an exciting step in your rose propagation journey, as you’ll soon be enjoying the beauty of your newly cultivated roses.
Determining When Cuttings Are Ready for Transplanting
Knowing when to transplant your rooted cuttings is crucial for their successful establishment. Here are key indicators:
- New Growth:Observe the cuttings for signs of vigorous new growth, indicating that they have successfully established a root system and are ready to thrive in the garden. This usually occurs after several weeks of rooting.
- Sturdy Roots:Gently pull on the cuttings to check for resistance. If they offer some resistance, it suggests a strong root system has formed, making them ready for transplanting.
- Root System Development:If you’re using clear containers for rooting, you can visually inspect the root system. When the roots have filled the container, it’s time to transplant.
Transplanting the Rooted Cuttings
Once your rose cuttings are ready for transplanting, follow these steps:
- Prepare the Planting Site:Choose a sunny location in your garden that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Prepare the soil by loosening it with a garden fork and incorporating compost or other organic matter to improve drainage and fertility.
- Dig a Hole:Dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of the cutting. The hole should be deep enough to accommodate the roots and allow for a slight mound of soil above the root ball after planting.
- Remove the Cutting:Carefully remove the rooted cutting from its rooting medium. Gently loosen the medium around the roots, being cautious not to damage them.
- Place in the Hole:Place the cutting in the prepared hole, ensuring that the graft union (the point where the cutting was taken from the parent plant) is slightly above the soil line.
- Backfill and Water:Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots. Water the cutting thoroughly to settle the soil and encourage root establishment.
- Mulch:Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the cutting to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Planting Cuttings in Their Permanent Location
When planting your rose cuttings in their permanent location, consider the following:
- Spacing:Space your rose cuttings according to the mature size of the variety. For example, hybrid tea roses typically need 3-4 feet of space between plants, while floribunda roses may require 2-3 feet.
- Sunlight:Ensure that the planting site receives adequate sunlight, as roses thrive in full sun.
- Soil:Roses prefer well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. If your soil is heavy clay, consider amending it with compost or other organic materials to improve drainage.
- Watering:Water your newly transplanted cuttings deeply and regularly, especially during the first few weeks after planting. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
Ongoing Care for New Rose Plants

Nurturing your newly rooted rose cuttings into thriving plants requires consistent care, particularly during the establishment phase. Providing the right balance of water, nutrients, and protection will help your roses develop strong root systems and robust growth.
Watering
Adequate watering is crucial for the successful establishment of your new rose plants. Rose cuttings require consistent moisture to promote root development and overall growth. Here are some key considerations for watering:
- Frequency:Water deeply but less frequently, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. This encourages deep root growth, which is essential for healthy roses.
- Watering Method:Water deeply at the base of the plant, avoiding getting the foliage wet. This minimizes the risk of fungal diseases.
- Timing:Early morning is the best time to water, as the water has time to soak in before the sun evaporates it.
- Mulching:A layer of mulch around the base of the plant helps retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Fertilizing
Roses are heavy feeders and benefit from regular fertilization to support their growth and flowering.
- Type of Fertilizer:Use a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for roses, containing a ratio of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) such as 10-10-10 or 20-10-20.
- Frequency:Fertilize your rose plants every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
- Application:Apply fertilizer around the base of the plant, avoiding direct contact with the stems.
Pruning, How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings: Transform Your Garden with Expert Tips
Pruning new rose plants helps to encourage branching, promote healthy growth, and shape the plant.
- Timing:Prune your rose plants in late winter or early spring, before new growth emerges.
- Technique:Remove any dead, diseased, or crossing branches. Pinch back the tips of new shoots to encourage bushier growth.
- Purpose:Pruning also helps to control the size and shape of the rose plant.
Common Problems
New rose plants are susceptible to certain problems that can hinder their growth and development. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Disease:Fungal diseases, such as black spot and powdery mildew, can affect new rose plants. Good air circulation, avoiding overhead watering, and using fungicides can help prevent these diseases.
- Pests:Aphids, spider mites, and rose slugs are common pests that can attack new rose plants. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to control these pests.
- Nutritional Deficiencies:Yellowing leaves can indicate a lack of nutrients, such as iron or magnesium. Apply a fertilizer specifically formulated to address these deficiencies.
Protecting from Pests and Diseases
Prevention is key to keeping your new rose plants healthy and thriving.
- Cleanliness:Keep your rose plants clean by removing any dead or diseased leaves or stems.
- Air Circulation:Ensure good air circulation around your rose plants by spacing them appropriately.
- Mulch:Use a layer of mulch around the base of the plant to suppress weeds and retain moisture.
- Resistant Varieties:Choose rose varieties known for their resistance to common pests and diseases.
Rose Propagation Tips for Success
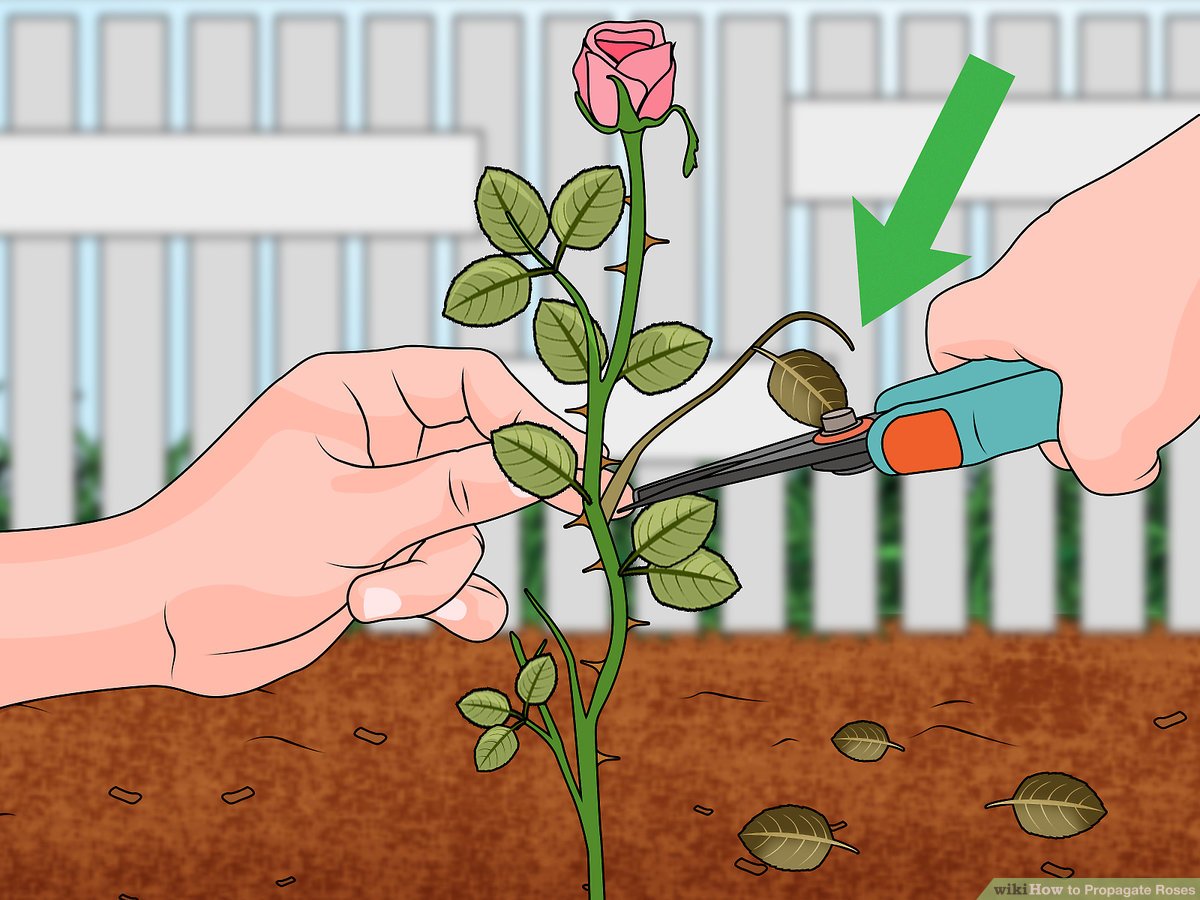
Propagating roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden. While success isn’t guaranteed, understanding the key factors and avoiding common mistakes can significantly increase your chances of success.
Factors for Successful Rose Propagation
Several factors contribute to successful rose propagation from cuttings. Understanding and implementing these factors can significantly increase your chances of success.
Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
Timing |
Propagate roses in spring or early summer when the plant is actively growing. Avoid late summer or fall as the plant prepares for dormancy. |
Cuttings Selection |
Choose healthy, disease-free cuttings from the current year’s growth. Select stems that are semi-hardwood, meaning they are firm but not fully woody. |
Cuttings Preparation |
Make clean cuts with a sharp knife or pruning shears. Remove leaves from the bottom inch or two of the cutting and trim any remaining leaves to reduce water loss. |
Rooting Medium |
Use a well-draining rooting medium like a mixture of perlite and peat moss or a commercial rooting mix. Ensure the medium is consistently moist but not soggy. |
Humidity and Temperature |
Provide high humidity to prevent cuttings from drying out. A humidity dome or plastic bag over the cuttings can help. Maintain a temperature between 70-75°F (21-24°C). |
Light |
Cuttings need bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. |
Patience |
Rose cuttings can take several weeks to several months to root. Be patient and avoid disturbing the cuttings during the rooting process. |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding and avoiding these common mistakes can significantly increase your chances of success in rose propagation.
- Using too old or too young cuttings:Choose cuttings from the current year’s growth that are semi-hardwood, meaning they are firm but not fully woody. Too old cuttings may be difficult to root, while too young cuttings are more prone to wilting.
- Making improper cuts:Use a sharp knife or pruning shears to make clean, angled cuts at the base of the cutting. Avoid crushing or damaging the stem.
- Overwatering:A well-draining rooting medium is crucial. Ensure the medium is consistently moist but not soggy. Overwatering can lead to root rot.
- Lack of humidity:High humidity is essential for successful rooting. A humidity dome or plastic bag can help maintain the appropriate humidity level.
- Too much direct sunlight:Cuttings need bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
- Disturbing the cuttings:Avoid disturbing the cuttings during the rooting process. Give them time to develop roots.
Successful Rose Propagation Examples
Successful rose propagation from cuttings has been achieved by many gardeners, proving that it is possible with proper techniques and patience.
- Example 1:A gardener successfully propagated a David Austin English rose from cuttings taken in late spring. The cuttings were rooted in a mixture of perlite and peat moss under a humidity dome. After 6 weeks, the cuttings had developed roots and were transplanted into individual pots.
- Example 2:A rose enthusiast successfully propagated a collection of hybrid tea roses using a rooting hormone and a well-draining potting mix. The cuttings were kept in a warm, humid environment and received bright, indirect light. After 8 weeks, the cuttings had developed roots and were transplanted into their permanent location in the garden.
Last Recap
With a little patience and the right techniques, propagating roses from cuttings can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the potential of these exquisite flowers, transforming your garden into a vibrant sanctuary of beauty.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a novice enthusiast, the art of rose propagation offers a unique opportunity to connect with nature and create a lasting legacy of floral splendor. So, gather your tools, choose your cuttings, and embark on this fascinating journey of transforming your garden with the elegance of homegrown roses.
Commonly Asked Questions
Can I propagate roses from any type of rose?
While most rose varieties can be propagated from cuttings, some types are more challenging than others. Hybrid teas and floribunda roses are generally easier to propagate, while species roses and some modern cultivars may require more specialized techniques.
What is the best time of year to take rose cuttings?
The ideal time to take rose cuttings depends on the type of cutting. Softwood cuttings are best taken in late spring or early summer, while hardwood cuttings are best taken in late fall or winter.
How long does it take for rose cuttings to root?
The time it takes for rose cuttings to root can vary depending on the variety, rooting method, and environmental conditions. Generally, it takes 4-6 weeks for softwood cuttings to root and 6-8 weeks for hardwood cuttings.
What are some common problems that can occur with new rose plants?
Common problems with new rose plants include root rot, fungal diseases, pests, and lack of nutrients. Proper watering, good drainage, and regular inspection for pests and diseases can help prevent these issues.