Best Lighting Conditions for Common Houseplants is a crucial factor in ensuring the health and vibrancy of your indoor greenery. Understanding the different types of light, their impact on plant growth, and the specific needs of various houseplants is essential for creating a thriving indoor garden.
From the bright, sun-loving succulents to the shade-tolerant ferns, each plant requires a particular light environment to flourish.
This guide delves into the world of light requirements for common houseplants, providing a comprehensive overview of light types, assessing your home’s lighting conditions, and identifying the ideal light needs for specific plants. We’ll explore practical tips for adjusting light levels, recognizing signs of improper lighting, and maximizing light exposure for optimal growth.
Additionally, we’ll discuss the benefits and considerations of using artificial light sources to supplement natural light.
Understanding Light Requirements

The amount and type of light a houseplant receives significantly impacts its growth and health. Understanding the different types of light and their effects on plants is crucial for providing optimal growing conditions.
Different Types of Light
Light intensity and duration play a vital role in plant growth. Here’s a breakdown of the common types of light encountered in homes:
- Direct Sunlight:Direct sunlight refers to the unfiltered rays of the sun that directly hit a plant. This type of light is the strongest and provides the most intense light intensity. It is typically found in south-facing windows.
- Indirect Sunlight:Indirect sunlight is sunlight that has been filtered through a window, curtain, or other object. It provides a softer, less intense light compared to direct sunlight. East- and west-facing windows often provide indirect sunlight.
- Low Light:Low light conditions refer to areas with minimal natural light exposure. These areas might receive only a few hours of indirect sunlight or primarily rely on artificial light sources.
- Artificial Light:Artificial light sources, such as fluorescent lights or LED grow lights, can be used to supplement or replace natural light. These lights can provide specific wavelengths and intensities suitable for plant growth.
Impact of Light on Plant Growth
The amount and type of light affect various aspects of plant growth, including:
- Photosynthesis:Plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars for growth and energy. Light intensity directly influences the rate of photosynthesis.
- Leaf Color:Plants that receive sufficient light often have vibrant, deep green leaves. Conversely, plants in low light conditions may develop paler leaves due to reduced chlorophyll production.
- Stem Length:Plants in low light tend to stretch towards light sources, resulting in elongated stems and weaker growth. Adequate light prevents excessive stretching and promotes compact growth.
- Flowering:Many flowering plants require a specific amount of light to initiate blooming. Inadequate light can delay or prevent flowering.
Examples of Houseplants for Different Light Conditions
Here are examples of common houseplants that thrive in various light conditions:
- Direct Sunlight:
- Succulents:Many succulents, such as cacti, aloes, and echeverias, thrive in bright, direct sunlight.
- Tropical Plants:Some tropical plants, including hibiscus, bougainvillea, and citrus trees, prefer full sun conditions.
- Indirect Sunlight:
- Snake Plant:Snake plants are known for their resilience and ability to tolerate low light conditions, but they prefer bright, indirect light.
- Peace Lily:Peace lilies thrive in bright, indirect light and can tolerate some shade.
- ZZ Plant:ZZ plants are highly adaptable and can tolerate a wide range of light conditions, including low light, but they prefer bright, indirect light.
- Low Light:
- Cast Iron Plant:As its name suggests, the cast iron plant is incredibly tolerant of low light conditions and can even survive in dimly lit rooms.
- Pothos:Pothos is a popular houseplant that can thrive in low light conditions, although it may grow more slowly.
- Spider Plant:Spider plants are adaptable and can tolerate low light conditions, but they prefer bright, indirect light for optimal growth.
Identifying the Best Lighting Conditions: Best Lighting Conditions For Common Houseplants
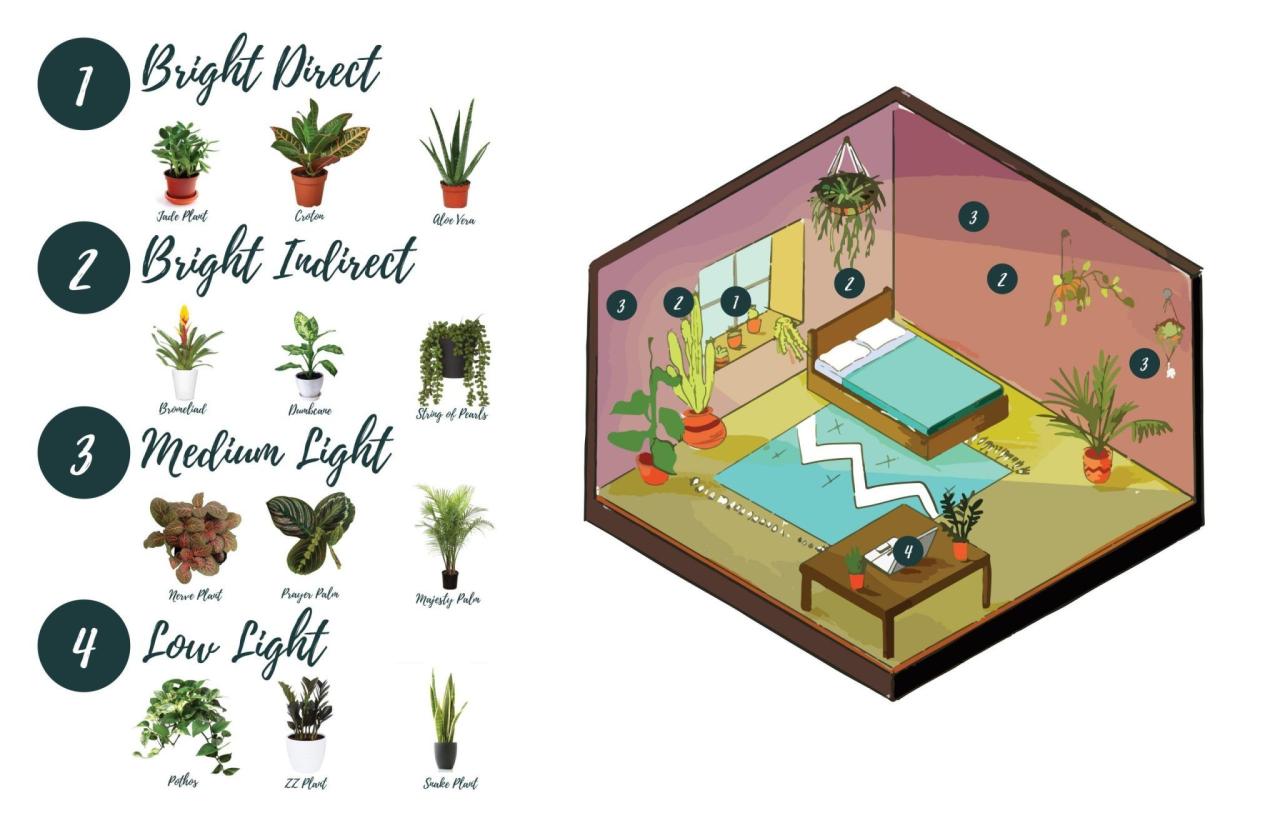
Knowing how much light your houseplants need is crucial for their health and growth. It’s like providing them with the right amount of food and water – the right lighting helps them thrive. Understanding how to assess your home’s light levels and match them to your plants’ needs is key to keeping them happy and vibrant.
Assessing Light Levels in Your Home
To determine the best lighting conditions for your houseplants, start by evaluating the light levels in your home. Here’s how to assess the light levels in your home:* Consider the direction of your windows:Windows facing south receive the most direct sunlight, followed by west, east, and then north-facing windows.
Observe the amount of sunlight
Pay attention to how much sunlight enters your home throughout the day. Direct sunlight is the strongest, followed by bright indirect light, then low light.
Understanding the best lighting conditions for common houseplants is crucial for their thriving. From the low-light tolerant Snake Plant to the sun-loving Fiddle Leaf Fig, each plant has its own unique needs. To discover which plants are best suited for your home, consult The Top 10 Most Popular Houseplants to Grow Indoors.
By matching the right plant with the appropriate lighting conditions, you can create a lush and vibrant indoor oasis.
Use a light meter
A light meter can provide accurate measurements of light levels, helping you determine if a spot is suitable for specific plants.
Feel the temperature
Direct sunlight can heat up a room significantly. If a spot feels warm to the touch, it’s likely receiving a lot of sunlight.
Determining Optimal Light Conditions for Specific Houseplants
Once you have a good understanding of the light levels in your home, you can start to match your plants to the appropriate spots.Here are some tips for determining the optimal light conditions for specific houseplants:* Read plant labels:Most houseplants come with care instructions that include their light requirements.
Consult online resources
Websites and books dedicated to houseplants provide detailed information on light needs.
Observe your plants
Pay attention to how your plants respond to different light levels. If they start to lose their color, grow leggy, or show signs of stress, it might be time to adjust their location.
Adjusting Light Levels for Houseplants
If you find that a particular spot doesn’t provide the right amount of light for your plants, you can adjust the light levels using curtains, blinds, or artificial light sources.* Curtains and Blinds:Curtains and blinds can help diffuse direct sunlight, creating brighter indirect light.
Artificial Light Sources
Artificial light sources, such as grow lights, can supplement natural light, especially during winter months or in rooms with limited natural light.
For example, if you have a plant that prefers bright indirect light but is currently in a spot that receives too much direct sunlight, you can use sheer curtains or blinds to diffuse the sunlight.
Common Houseplants and Their Light Needs

Now that you understand the basics of light requirements and how to identify the best lighting conditions for your home, let’s explore some popular houseplants and their specific light needs.
Common Houseplants and Their Light Needs
This table provides a comprehensive overview of common houseplants and their light requirements, along with additional care tips to ensure their thriving.
Plant Name |
Common Name |
Light Requirement |
Additional Care Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
Aspidistra elatior |
Cast Iron Plant |
Low Light |
Tolerates neglect, infrequent watering, and low humidity. |
Chlorophytum comosum |
Spider Plant |
Low to Medium Light |
Easy to propagate, thrives in bright indirect light, and tolerates some dryness. |
Sansevieria trifasciata |
Snake Plant |
Low Light |
Water sparingly, allowing soil to dry completely between waterings, and prefers bright indirect light. |
ZZ Plant |
Zamioculcas zamiifolia |
Low Light |
Extremely drought-tolerant, prefers indirect light, and tolerates low humidity. |
Pothos |
Epipremnum aureum |
Low to Medium Light |
Easy to care for, prefers bright indirect light, and can tolerate some neglect. |
Peace Lily |
Spathiphyllum wallisii |
Medium Light |
Prefers bright indirect light, needs consistently moist soil, and enjoys high humidity. |
Chinese Evergreen |
Aglaonema |
Medium Light |
Tolerates low light, prefers bright indirect light, and requires consistently moist soil. |
Philodendron |
Various species |
Medium Light |
Prefers bright indirect light, enjoys consistently moist soil, and can tolerate some neglect. |
Monstera deliciosa |
Swiss Cheese Plant |
Medium to High Light |
Prefers bright indirect light, needs consistently moist soil, and enjoys high humidity. |
Fiddle Leaf Fig |
Ficus lyrata |
High Light |
Prefers bright indirect light, needs consistently moist soil, and enjoys high humidity. |
Bird of Paradise |
Strelitzia reginae |
High Light |
Prefers bright indirect light, needs consistently moist soil, and enjoys high humidity. |
Signs of Improper Lighting
It is important to understand the signs of improper lighting for your houseplants, as they can indicate a need for adjustment in their environment. These signs can range from subtle changes in growth patterns to more obvious visual cues, and recognizing them is crucial for ensuring the health and vitality of your plants.
By observing these signs and adjusting the lighting conditions accordingly, you can provide your houseplants with the optimal environment they need to thrive. Understanding these indicators will empower you to become a more attentive and effective plant parent.
Signs of Under-Lighting
Under-lighting occurs when a plant does not receive enough light to sustain its growth processes. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including stunted growth, pale foliage, and elongated stems. Identifying these signs is crucial for providing the necessary light for your plant’s optimal health and development.
- Stunted Growth:Plants deprived of adequate light will exhibit slow growth, with new leaves smaller than usual and fewer new leaves emerging.
- Pale Foliage:Under-lit plants will often have leaves that are paler than normal, lacking the vibrant green color characteristic of healthy plants. This is due to reduced chlorophyll production, essential for photosynthesis.
- Elongated Stems:Plants reach for light sources, leading to elongated stems with larger gaps between leaves. This is a common sign of stretching for more light.
- Leaf Drop:In some cases, under-lit plants may drop leaves to conserve energy, particularly if the situation persists.
- Yellowing Leaves:While yellowing leaves can be caused by various factors, under-lighting can contribute to this issue, particularly if accompanied by other signs.
Signs of Over-Lighting
Over-lighting occurs when a plant receives too much light, potentially leading to damage and stress. This can manifest in various ways, including leaf scorch, discoloration, and wilting. Identifying these signs is important for ensuring your plants are not exposed to excessive light levels.
- Leaf Scorch:Over-exposed plants may develop brown, crispy spots or edges on their leaves, indicating sun damage. This is often seen on leaves directly facing strong sunlight.
- Discoloration:Excessive light can cause leaves to turn yellow, white, or even red, as the plant tries to protect itself from damage.
- Wilting:Over-lit plants may wilt due to excessive water loss through transpiration, as the intense light increases evaporation from the leaves.
- Leaf Drop:Over-lighting can also cause leaves to drop, as the plant tries to reduce its surface area exposed to the intense light.
- Stunted Growth:While under-lighting often leads to stunted growth, over-lighting can also cause stunted growth, as the plant struggles to cope with the stress.
Diagnosing and Adjusting Lighting Conditions, Best Lighting Conditions for Common Houseplants
Once you’ve identified signs of improper lighting, it’s crucial to diagnose the specific issue and adjust the lighting conditions accordingly. This involves analyzing the plant’s current environment, considering its light needs, and implementing appropriate solutions.
Understanding the best lighting conditions for common houseplants is crucial for their health and growth. Many popular indoor plants thrive in bright, indirect light, but some, like the Snake Plant and ZZ Plant, tolerate low light conditions. These plants also happen to be excellent air purifiers, making them ideal choices for homes seeking cleaner air.
For a comprehensive guide on the best houseplants for air purification, check out The Best Common Houseplants for Air Purification. Once you’ve chosen your plants, be sure to provide them with the appropriate light levels to ensure their well-being and air-purifying abilities.
- Analyze the Plant’s Environment:Carefully observe the plant’s location, including the amount of natural light it receives, the presence of artificial light sources, and any obstructions that may be blocking light.
- Consider the Plant’s Light Needs:Research the specific light requirements of your plant. Some plants thrive in bright, direct sunlight, while others prefer indirect light or even low-light conditions.
- Adjust Lighting Conditions:Based on your diagnosis, adjust the lighting conditions to provide the optimal environment for your plant. This may involve relocating the plant to a brighter or shadier spot, using artificial light sources, or adjusting the duration of light exposure.
Addressing Under-Lighting
If you’ve identified signs of under-lighting, there are several steps you can take to provide your plant with more light.
- Relocate the Plant:Move the plant to a brighter location, ideally near a window that receives ample natural light.
- Use Artificial Light:Supplement natural light with artificial light sources, such as grow lights or fluorescent bulbs. Choose bulbs specifically designed for plant growth, and ensure they are placed at the appropriate distance from the plant.
- Rotate the Plant:Rotate the plant regularly to ensure all sides receive equal light exposure. This helps prevent uneven growth and promotes healthy development.
Addressing Over-Lighting
If your plant is exhibiting signs of over-lighting, there are steps you can take to reduce its exposure to excessive light.
- Relocate the Plant:Move the plant to a shadier location, away from direct sunlight. This could involve placing it further from the window or behind a sheer curtain.
- Use a Diffuser:Place a sheer curtain or a diffuser over the window to soften the sunlight and reduce its intensity.
- Adjust the Time of Day:Avoid exposing the plant to direct sunlight during the hottest part of the day, especially in the summer.
Optimizing Light for Plant Growth
Providing the right amount of light is crucial for the health and well-being of your houseplants. Optimal lighting conditions ensure proper photosynthesis, leading to vibrant foliage, robust growth, and even beautiful blooms.
Maximizing Light Exposure
Maximizing light exposure without harming your plants involves understanding their specific needs and implementing strategies that enhance their light intake without causing damage.
- Rotate Plants Regularly:Rotating your plants regularly ensures that all sides receive equal exposure to light, preventing uneven growth and promoting balanced development.
- Utilize Light Reflectors:Reflectors, such as white surfaces or mirrors placed strategically near your plants, can bounce light back onto their leaves, increasing overall light exposure.
- Consider Plant Placement:Position plants near windows, especially south-facing ones, to maximize natural light.
Creative Ways to Enhance Light Levels
To create optimal lighting conditions, especially in areas of the home with limited natural light, consider these creative solutions:
- Grow Lights:Artificial grow lights, designed to mimic the spectrum of sunlight, provide a controlled and consistent source of light, particularly beneficial during winter months or in rooms with minimal natural light.
- Light-Reflecting Surfaces:Utilizing light-reflecting surfaces, such as white walls or mirrors, can enhance the brightness of a room and increase the amount of light reaching your plants.
- Window Placement:Strategically positioning plants near windows, even if they don’t receive direct sunlight, can significantly improve their light exposure.
Artificial Lighting for Houseplants
Artificial light can be a valuable tool for providing the necessary light for indoor plants, especially when natural light is limited. It allows you to cultivate a variety of plants in different environments, including homes, offices, and even indoor gardens.
Types of Artificial Light Sources
Artificial light sources offer different spectrums and intensities, impacting plant growth.
- Incandescent Bulbs:These traditional bulbs emit a warm, yellowish light that is not ideal for plant growth. They produce a lot of heat, which can be detrimental to plants, especially those sensitive to high temperatures. They are also inefficient, converting most of their energy into heat rather than light.
- Fluorescent Bulbs:These bulbs offer a more efficient and cooler light source than incandescent bulbs. They come in various color temperatures, with cool white and daylight being more suitable for plant growth. However, fluorescent bulbs may not provide the full spectrum of light that plants need, particularly in the red and blue wavelengths.
- LED Grow Lights:LED grow lights are becoming increasingly popular for indoor plant cultivation. They offer several advantages, including energy efficiency, long lifespan, and customizable light spectrums. LEDs emit light in specific wavelengths that are essential for photosynthesis, promoting healthy growth and flowering.
They also produce less heat than other light sources, making them safer for plants.
- High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lights:HID lights, including metal halide and high-pressure sodium lamps, are powerful and efficient light sources. They are often used in commercial greenhouses and indoor gardens due to their high light output. However, they require special fixtures and can generate significant heat, making them less suitable for home use.
Comparing the Effectiveness of Light Sources
The effectiveness of artificial light sources depends on factors such as the plant species, the light intensity, and the duration of exposure.
Light Source |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
Incandescent Bulbs |
Affordable, readily available |
Inefficient, produces excessive heat, poor light quality for plants |
Fluorescent Bulbs |
More efficient than incandescent, cooler light, available in various color temperatures |
May not provide the full spectrum of light needed for plants |
LED Grow Lights |
Energy efficient, long lifespan, customizable light spectrums, less heat production |
More expensive than other options |
HID Lights |
Powerful and efficient, high light output |
Requires special fixtures, generates significant heat, not suitable for home use |
Choosing the Right Artificial Light for Specific Houseplants
When selecting artificial lighting for your houseplants, consider the plant’s specific light requirements.
- Low-Light Plants:These plants can tolerate low light conditions and often thrive with indirect sunlight or artificial light sources like fluorescent bulbs or LED grow lights with a low intensity setting.
- Medium-Light Plants:These plants require brighter light but can still tolerate some shade. Fluorescent bulbs, LED grow lights with a medium intensity setting, or a combination of natural and artificial light can be suitable for these plants.
- High-Light Plants:These plants need bright light, ideally with direct sunlight for several hours daily. For these plants, LED grow lights with a high intensity setting or a combination of natural and artificial light is recommended.
Final Thoughts
By understanding the nuances of light and its impact on houseplants, you can create a thriving indoor oasis that brings joy and beauty to your home. From identifying the right light conditions to implementing practical solutions, this guide empowers you to provide your plants with the light they need to thrive.
With a little knowledge and attention, you can transform your home into a botanical paradise where your houseplants flourish and bring a touch of nature indoors.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the best ways to measure light levels in my home?
You can use a light meter specifically designed for plants, or you can rely on visual cues. Observe the amount of sunlight entering your home throughout the day, noting the duration and intensity. Consider factors like window size, direction, and any obstructions.
Can I use grow lights for all my houseplants?
While grow lights can be beneficial, they are not always necessary. Some plants thrive in natural light, while others may require additional light support. Choose grow lights based on the specific needs of your plants and their light requirements.
How often should I rotate my houseplants to ensure even light exposure?
Rotating your houseplants regularly, ideally every few weeks, helps ensure that all sides receive equal light exposure and promotes balanced growth. This is particularly important for plants placed near windows where light tends to be directional.
